HOME
HOME- Skin Condition
Lipoma
Lipoma

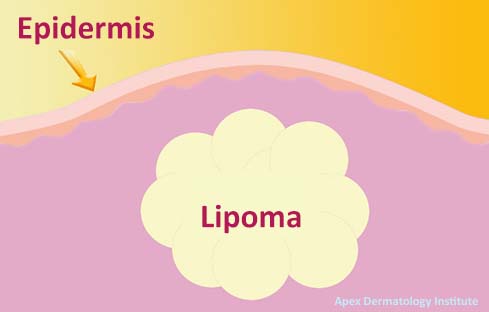
Lipoma is a benign (noncancerous) soft tissue tumor that primarily consists of adipocytes, which are fat cells. These growths can occur anywhere on the body but are most commonly found in the subcutaneous layer, situated between the skin and underlying muscle. Lipomas are generally slow-growing and typically present as palpable, painless, mobile, and rubbery masses under the skin. They can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Although the exact cause of lipoma formation remains unknown, various factors are believed to contribute to their development.

 Genetic predisposition: A hereditary component has been observed in cases of familial multiple lipomatosis, a condition characterized by the presence of multiple lipomas. Specific gene mutations or chromosomal abnormalities may lead to an increased likelihood of developing lipomas.
Genetic predisposition: A hereditary component has been observed in cases of familial multiple lipomatosis, a condition characterized by the presence of multiple lipomas. Specific gene mutations or chromosomal abnormalities may lead to an increased likelihood of developing lipomas.
 Mechanical trauma: In some instances, lipomas have been reported to develop following mechanical injury or trauma to the affected area. This suggests that localized tissue damage may trigger lipoma formation in certain individuals.
Mechanical trauma: In some instances, lipomas have been reported to develop following mechanical injury or trauma to the affected area. This suggests that localized tissue damage may trigger lipoma formation in certain individuals.
 Hormonal influences: Adipocytes, the primary cell type in lipomas, are influenced by hormonal factors. It has been hypothesized that hormonal imbalances or fluctuations might play a role in lipoma development, although a definitive link is yet to be established.
Hormonal influences: Adipocytes, the primary cell type in lipomas, are influenced by hormonal factors. It has been hypothesized that hormonal imbalances or fluctuations might play a role in lipoma development, although a definitive link is yet to be established.
 Metabolic disorders: Certain metabolic conditions, such as obesity or hyperlipidemia, may increase the risk of lipoma development due to the higher number of adipocytes present in the body.
Metabolic disorders: Certain metabolic conditions, such as obesity or hyperlipidemia, may increase the risk of lipoma development due to the higher number of adipocytes present in the body.
Lipoma Treatment

 Surgical Excision Procedure
Surgical Excision Procedure
Although they usually do not cause significant health issues, some individuals may opt for treatment due to cosmetic concerns or discomfort caused by the lipoma's location or size. The most common and definitive treatment for lipoma removal is surgical excision. This procedure involves making an incision, removing the entire lipoma, and closing the skin with sutures. This method provides a high success rate with low recurrence chances, but it comes with potential risks such as scarring and infection.
Factors such as the lipoma's size, location and growth pattern will influence the choice of treatment. Discuss with your dermatologist today and seek help to determine the most suitable option for your condition.